MOHID Land
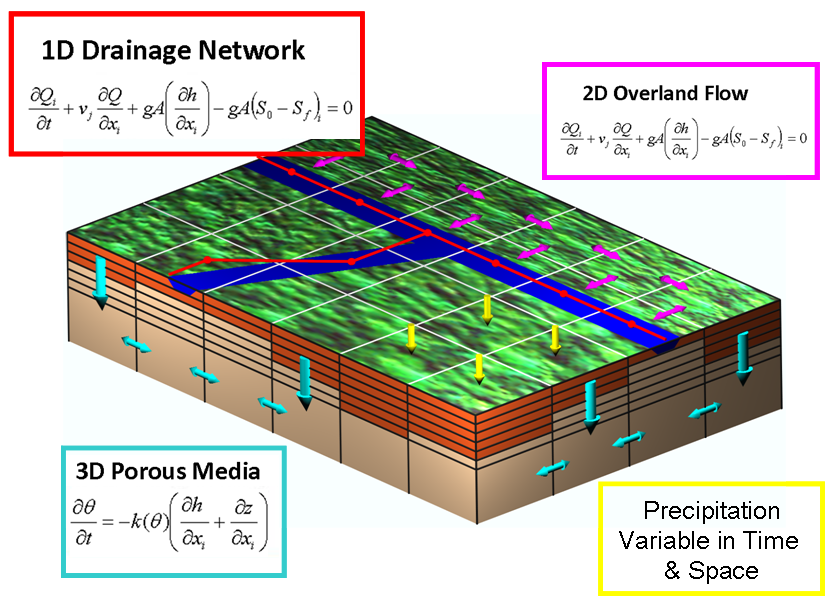
MOHID Land is a physically-based, spatially distributed, continuous, variable time step model for the water and property cycles in inland waters and main mediums and equations are presented in the image.
MOHID Land is an integrated model with four compartments or mediums (atmosphere, porous media, soil surface, and river network). Water moves through the mediums based on mass and momentum conservation equations. The atmosphere is not explicitly simulated but provides data necessary for imposing surface boundary conditions to the model (precipitation, solar radiation, wind, etc.) that may be space and time variant. The model is based on finite-volumes organized into a structured grid, rectangular in the horizontal plane, and Cartesian type in the vertical plane. Surface land is described by a 2D horizontal grid and the porous media is a 3D domain which includes the same horizontal grid as the surface complemented with a vertical grid with variable layer thickness. The river network is a 1D domain defined from the digital terrain model (DTM), with reaches linking surface cell centers. Fluxes are computed over the faces of the finite volumes and state variables are computed at the centre to assure conservation of transported properties. The model uses an explicit algorithm with a variable time step, that is maximum during dry season when fluxes are reduced and minimum when fluxes increase (e.g. during rain events).
Numerical Characteristics
Main Characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Spatial Discretisation | Finite volumes |
| Horizontal Grid | Orthogonal |
| Vertical Grid | Generic coordinates |
| Computation points distribution | Arakawa C |
| Time discretisation |
|
Main Processes | |
|---|---|
| Atmosphere | Can be forced with field data (monitoring stations) or meteorological models (HDF). Atmosphere properties can be interpolated spatially and temporally from station data |
| Porous Media |
|
| Surface Water |
|
| Infiltration | Soil Conservation Service (SCS) Curve Number, Green Ampt equation and Richards equation |
| Evapotranspiration | Penman Monteith and water availability in soil |
| Plant dynamics | Plant growth and agricultural practices (planting, harvest, kill, fertilization, pesticide application, etc.) including dormancy and SWAT crop database |
| Reservoirs | Drainage Network and Reservoir interaction to account river flow impact due to man-made hydraulic infrastructures |
| Mediums Interface | Porous Media and Run-off interaction with Drainage Network is done using continuity equation (surface gradient between Run-off and Drainage Network, Richard's equation with level gradient between Porous Media and Drainage Network). |
| Time Step | Variable time step adapted to fluxes magnitude and/or Courant number to assure stability in high fluxes and reduce simulation time during low fluxes |


